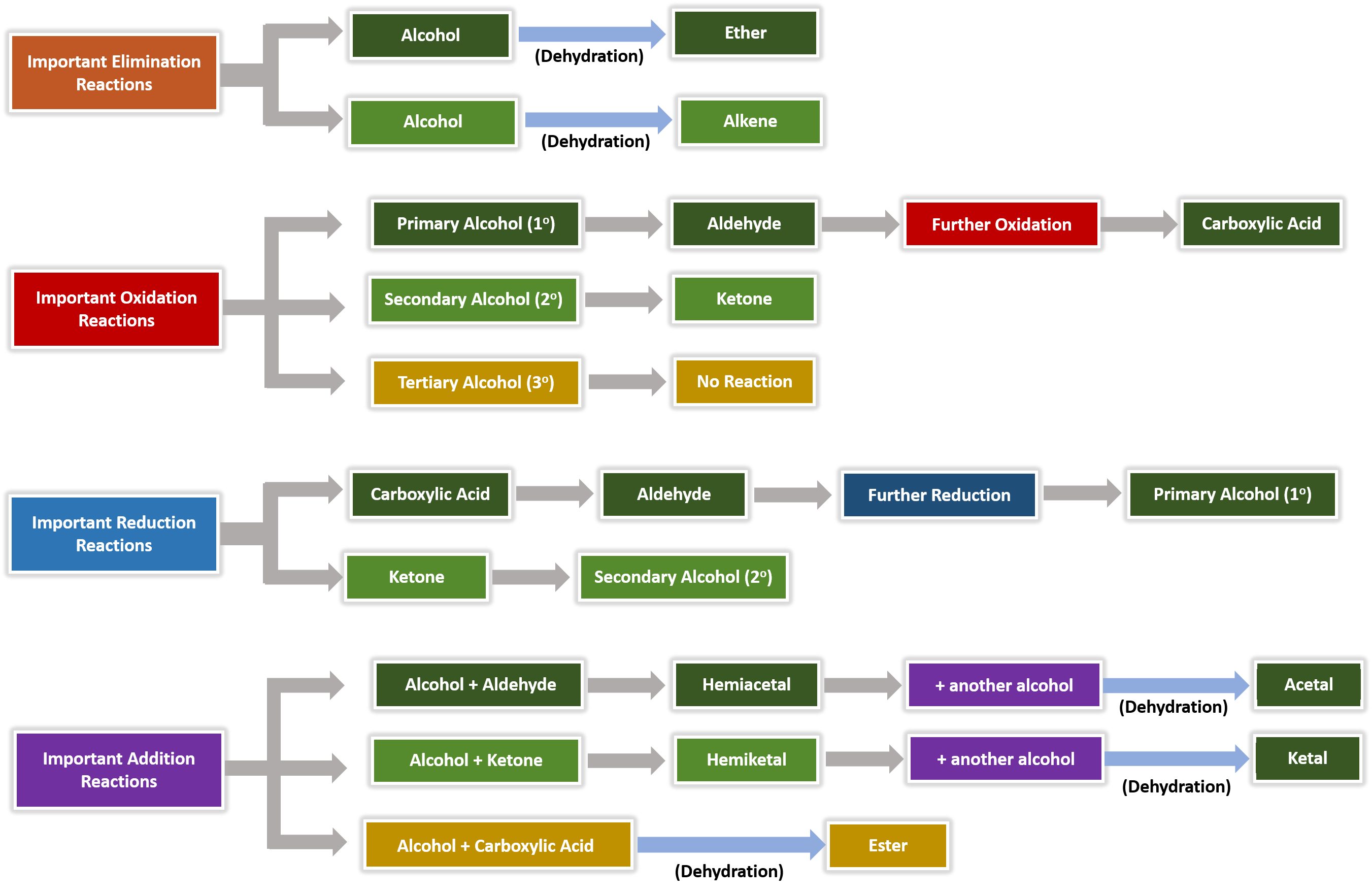
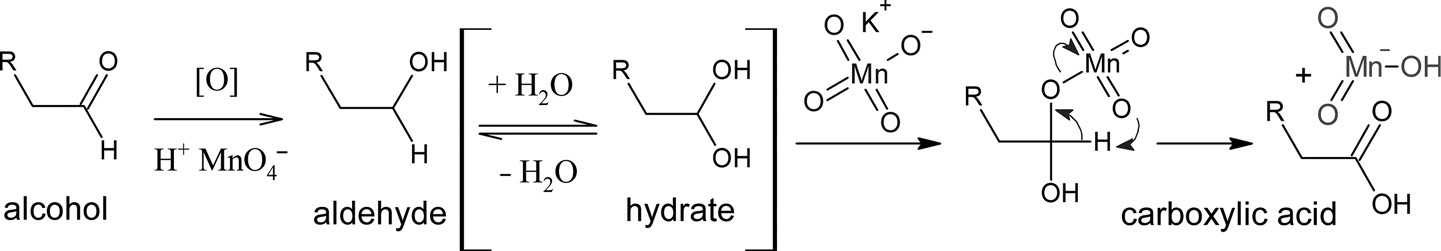
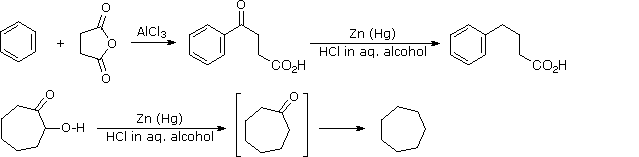
Chromium is in oxidation level six in dichromates and it is reduced to oxidation level three in this process The details of the reduction of chromate are complex, and we will not be concerned with them The oxidation of aldehydes also produces carboxylic acids, but since aldehydes are less readily made than carboxylic acids, this process isThis reduction stops at the aldehyde stage, providing us with a useful twostep procedure for converting carboxylic acids to aldehydes, as reaction #1 below demonstrates Equivalent reductions of anhydrides have not been reported, but we might speculate that they would be reduced more easily than estersAnother class of organic molecules contains a carbon atom connected to an oxygen atom by a double bond, commonly called a carbonyl group The trigonal planar carbon in the carbonyl group can attach to two other substituents leading to several subfamilies (aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters) described in this section
Ch105 Chapter 9 Organic Compounds Of Oxygen Chemistry
Aldehydes are more reduced than carboxylic acids
Aldehydes are more reduced than carboxylic acids-Free PDF download of Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids 5 Marks Questions prepared by expert Chemistry teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books On CoolGyanOrg to score more marks in CBSE board examinationAldehydes are more easily reduced than the carboxylic acids, and LiAlH4 reduces all the way back to 1° alcohols 5721 Reduction of acid chlorides Preparation of primary alcohols Acid chlorides are easy to reduce than carboxylic acids and other carboxylic acid derivatives


Chapter 4 Carboxylic Acids Esters Che 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library
Aldehydes and Ketones Both aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, a functional group with a carbonoxygen double bondThe names for aldehyde and ketone compounds are derived using similar nomenclature rules as for alkanes and alcohols, and include the classidentifying suffixes al and one, respectively In an aldehyde, the carbonyl group is bonded to at least one hydrogen atomThe direct reduction of carboxylic acids to aldehydes is a fundamental transformation in organic synthesis The combination of an airstable Ni precatalyst, dimethyl dicarbonate as an activator, and silane reductant effects this reduction for a wide variety of substrates, including pharmaceutically relevant structures, in good yields and with no overreduction to alcoholsExample 1 Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry Methane represents the completely reduced form of an organic molecule that contains one carbon atom Sequentially replacing each of the carbonhydrogen bonds with a carbonoxygen bond would lead to an alcohol, then an aldehyde, then a carboxylic acid (discussed later), and, finally, carbon dioxide
Balbharati solutions for Chemistry 12th Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 12 (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids) include all questions with solution and detail explanation This will clear students doubts about any question and improve application skills while preparing for board exams The detailed, stepbystep solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clearAldehydes and ketone vary in their oxidation reactions but aldehydes can easily undergo this process to form carboxylic acids with known oxidizing agents such as potassium dichromate, potassium permanganate, and nitric acid, etcMoreover, the oxidizing agents with a mild property such as Tollen's reagents and Fehling's reagent are alsoAldehydes and Ketones from Acid Chlorides Aldehydes It is very difficult to reduce a carboxylic acid back to an aldehyde and to get the reduction to stop there Aldehydes themselves are very easily reduced (more reactive than acids), and so almost always, overreduction occurs
Physical and Chemical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones In many of the reactions, ketones and aldehydes are the same as both of them have the carbonyl functional group In the most important types of reactions such as oxidation, they differ greatly Ketones resist the oxidation, whereas aldehydes are readily oxidized to the carboxylic acidsReductions of carboxylic acid derivatives might be expected to lead either to aldehydes or alcohols, functional groups having a lower oxidation state of the carboxyl carbon Indeed, carboxylic acids themselves are reduced to alcohols by lithium aluminum hydride At this point it will be useful to consider three kinds of reductionsThe aromatic carboxylic acids are practically insoluble in cold water, whereas all the carboxylic acids are soluble in the organic solvents like ether, alcohol, benzene, and more Carboxylic acids are the most acidic among the organic acids, but they are less acidic than mineral acids, namely sulphuric acid and nitric acid


Lecture 21



10
Read PDF Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Iecqa from an aldehyde, you can quite easily produce relatively complicated molecules like 2amino acids the amino acids which are used to construct proteins addition to aldehydes and ketones chemguide Carboxylic acids C n H 2n1 COOH COOH Those with only carboncarbon single bonds are3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to Describe the structure and properties of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters;In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the organic reduction of any carbonyl group by a reducing agent Typical carbonyl compounds are ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent;


Highly Chemoselective Step Down Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aromatic Hydrocarbons Via Palladium Catalysis Chemical Science Rsc Publishing



21 Ketones Are Easily Reduced To Secondary Alcohols B Primary Ch Cch A Secondary Alcohol Alcohol C To Homeworklib
Carboxylic acids, acid halides, esters, and amides are easily reduced by strong reducing agents, such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4)The carboxylic acids, acid halides, and esters are reduced to alcohols, while the amide derivative is reduced to an amineEsters or carboxylic acids cannot be reduced to aldehydes by hydride reducing agents because aldehydes are more reactive than esters or carboxylic acids Acid chlorides are more reactive than esters toward nucleophilic hydride ion As a result, acid chlorides are more rapidly reduced than esters However, lithium aluminum hydride is such a strong reducing agent that acid chlorides are still reduced all the way to primary alcoholsThe hydrogen atom in the functional group of a carboxylic acid will react with a base to form an ionic salt Carboxylic acids are weak acids (see the chapter on acids and bases), meaning they are not 100% ionized in water Generally only about 1% of the molecules of a carboxylic acid dissolved in water are ionized at any given time


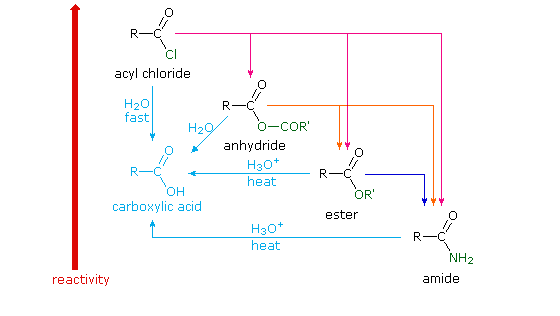
Carboxylic Acid Reactivity



11 4 The Relative Reactivity Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Chemistry Libretexts
Although carboxylic acids are more difficult to reduce than aldehydes and ketones, there are several agents that accomplish this reduction, the most important being lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4) and borane (BH 3)Another class of organic molecules contains a carbon atom connected to an oxygen atom by a double bond, commonly called a carbonylThey are more oxidized then alcohols but less oxidized than carboxylic acids Fact Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids or reduced to alcohols Ketones can be reduced to alcohols Aldehydes/Ketones > Alkanes Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acids, Esters, Amines, Amides 43 terms


Ch Carboxylic Acid Derivatives


Highly Chemoselective Step Down Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aromatic Hydrocarbons Via Palladium Catalysis Chemical Science Rsc Publishing
Carboxylic acids, acid halides, esters, and amides are easily reduced by strong reducing agents, such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4)The carboxylic acids, acid halides, and esters are reduced to alcohols, while the amide derivative is reduced to an amine3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to Describe the structure and properties of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters;Carboxylic acids, acid halides, esters, and amides are easily reduced by strong reducing agents, such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4)The carboxylic acids, acid halides, and esters are reduced to alcohols, while the amide derivative is reduced to an amine



Carbonyl Reduction Wikipedia



Lialh4 Nabh4 Dibal Reduction Summary For Aldehydes Ketones Esters And Carboxylic Acids Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry
An aldehyde is produced as an intermediate during this reaction, but it cannot be isolated because it is more reactive than the original carboxylic acid Esters can be converted to 1 o alcohols using LiAlH 4 , while sodium borohydride (latex NaBH_4 /latex) is not a strong enough reducing agent to perform this reactionThe hydrogen atom in the functional group of a carboxylic acid will react with a base to form an ionic salt Carboxylic acids are weak acids (see the chapter on acids and bases), meaning they are not 100% ionized in water Generally only about 1% of the molecules of a carboxylic acid dissolved in water are ionized at any given timeThe hydrogen atom in the functional group of a carboxylic acid will react with a base to form an ionic salt Carboxylic acids are weak acids (see the chapter on acids and bases), meaning they are not 100% ionized in water Generally only about 1% of the molecules of a carboxylic acid dissolved in water are ionized at any given time



Stereospecific Reduction Of Benzil With Sodium Borohydride


Fats Soaps
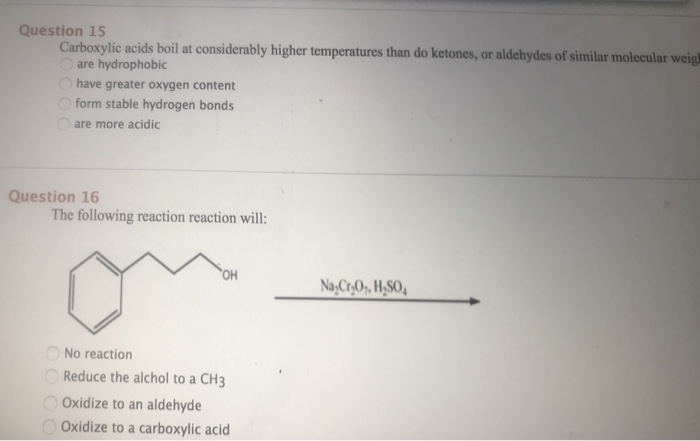
Reductions of carboxylic acid derivatives might be expected to lead either to aldehydes or alcohols, functional groups having a lower oxidation state of the carboxyl carbon Indeed, it was noted earlier that carboxylic acids themselves are reduced to alcohols by lithium aluminum hydride At this point it will be useful to consider three kinds of reductionsThe aromatic carboxylic acids are practically insoluble in cold water, whereas all the carboxylic acids are soluble in the organic solvents like ether, alcohol, benzene, and more Carboxylic acids are the most acidic among the organic acids, but they are less acidic than mineral acids, namely sulphuric acid and nitric acidThus, aldehydes and ketones have higher boiling points compared to the hydrocarbons having the same weight


Carboxylic Acid And Esters Are Less Reactive To Nu Than Aldehydes Or Ketones Why Quora


Chapter 17
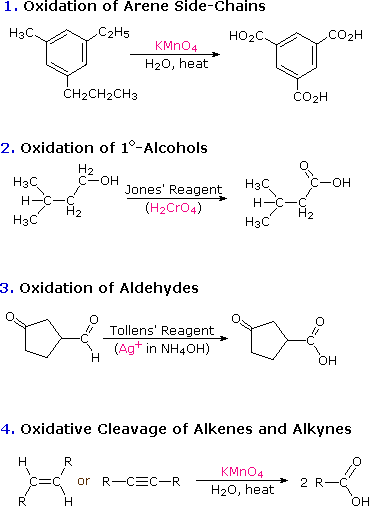
More polar than alcohols, un/saturated hydrocarbons, aldehydes and ketones CO and OH are both polar Very high melting and boiling points, up to 9 carbons are liquids, readily hydrogen bond to water molecules, short chains are miscible in waterTherefore, aldehydes reduce more easily than ketones and require milder reagents and milder conditions Carboxylic acids and esters are further stabilized by the presence of a second oxygen atom which can donate a lone pair into the already polar C=O bondThe carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones are reduced to – CH 2 – group on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with KOH in high boiling solvent such as ethylene glycol (3) Oxidation Oxidation of aldehyde gives carboxylic acids with same number of carbon atoms The common oxidising agents used are HNO 3, KMnO 4, K 2 Cr 2 O 7



Does Dibal H Reduce Carboxylic Acids Chemistry Stack Exchange


Magnetic Nanoparticle Functionalization Chapter 3 Magnetic Nanoparticles In Biosensing And Medicine
The carboxylic acids liberate hydrogen on reaction with electropositive metals like sodium Strength of acid is indicated by pKa value, which is given as, pKa = – logKa Smaller the pKa value, stronger is the acid Carboxylic acids are weaker acids than mineral acids but stronger acids than phenols because the carboxylate ion is moreMore polar than alcohols, un/saturated hydrocarbons, aldehydes and ketones CO and OH are both polar Very high melting and boiling points, up to 9 carbons are liquids, readily hydrogen bond to water molecules, short chains are miscible in waterAldehydes are more reactive than ketones (chapter 17) as they are less hindered and the alkyl group in the ketone is a weak electron donor Under the reaction condition s the carboxylic acid will deprotonate to give the carboxylate which is a very poor electrophile (after all, it has a negative charge !) so the ester is more reactive than the acid



Solved 15 Consider Propanal Aldehyde And Propanoic Aci Chegg Com



10
So aldehydes and ketones have a trigonal planar arrangement around the carbonyl carbon atom The carbonyl group is a polar group (electronegativity of oxygen is larger than carbon, therefore, carbonyl group has a large dipole moment);One molecule of aldehyde is reduced to alcohol and the other is oxidized to carboxylic acid, in this reaction For example, ethanol and potassium ethanoate are produced when ethanol is treated with concentrated potassium hydroxideAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids's Previous Year Questions with solutions of Chemistry from JEE Main subject wise and chapter wise with solutions COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the compound obtained will be AIEEE 03 (More than One Correct Answer) More


Carboxyl Derivative Reactivity



Solved 3 Aldehydes And Ketones Shown Below Undergo Nuc Chegg Com
Another class of organic molecules contains a carbon atom connected to an oxygen atom by a double bond, commonly called a carbonylAldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcoholsAnother class of organic molecules contains a carbon atom connected to an oxygen atom by a double bond, commonly called a carbonyl
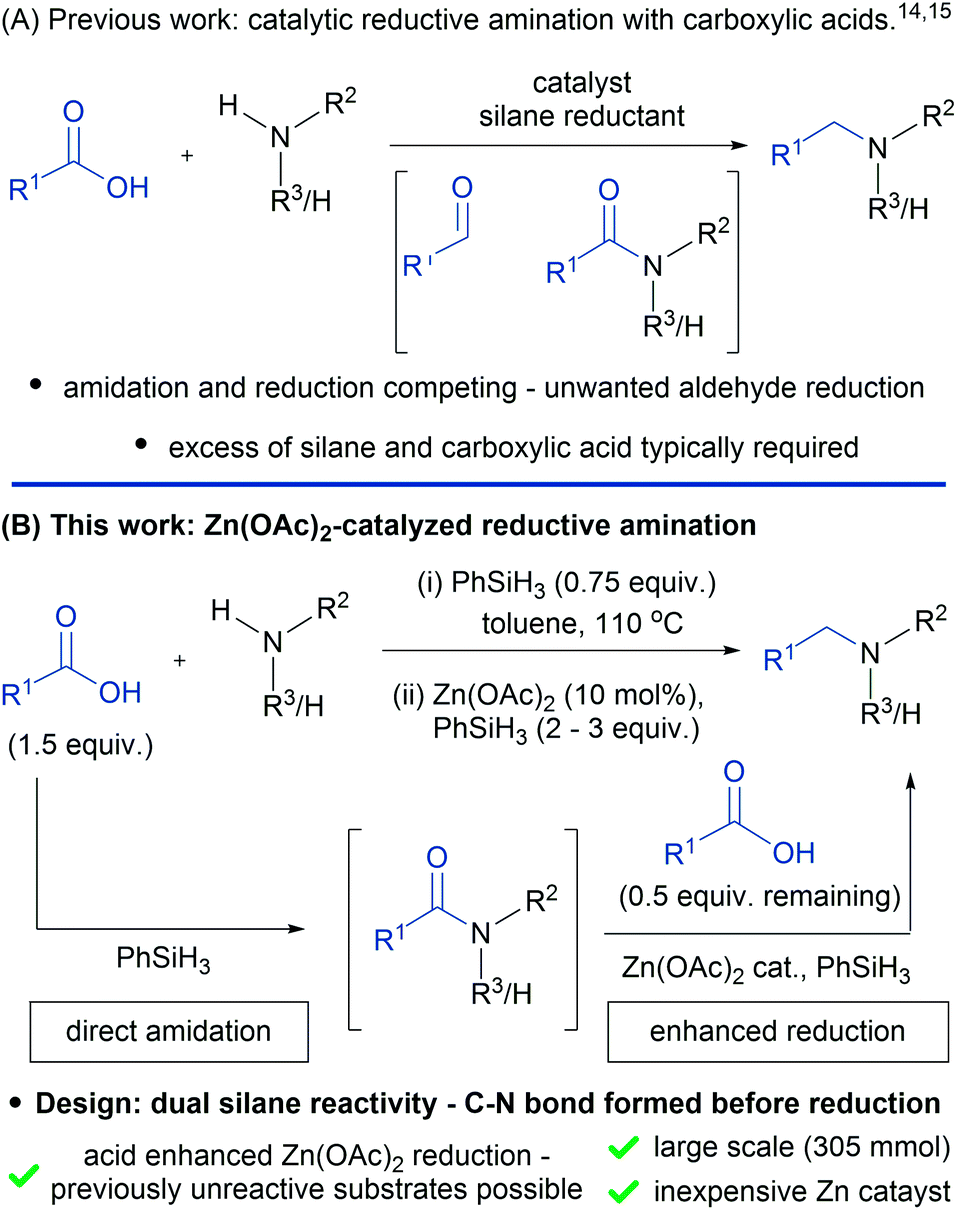


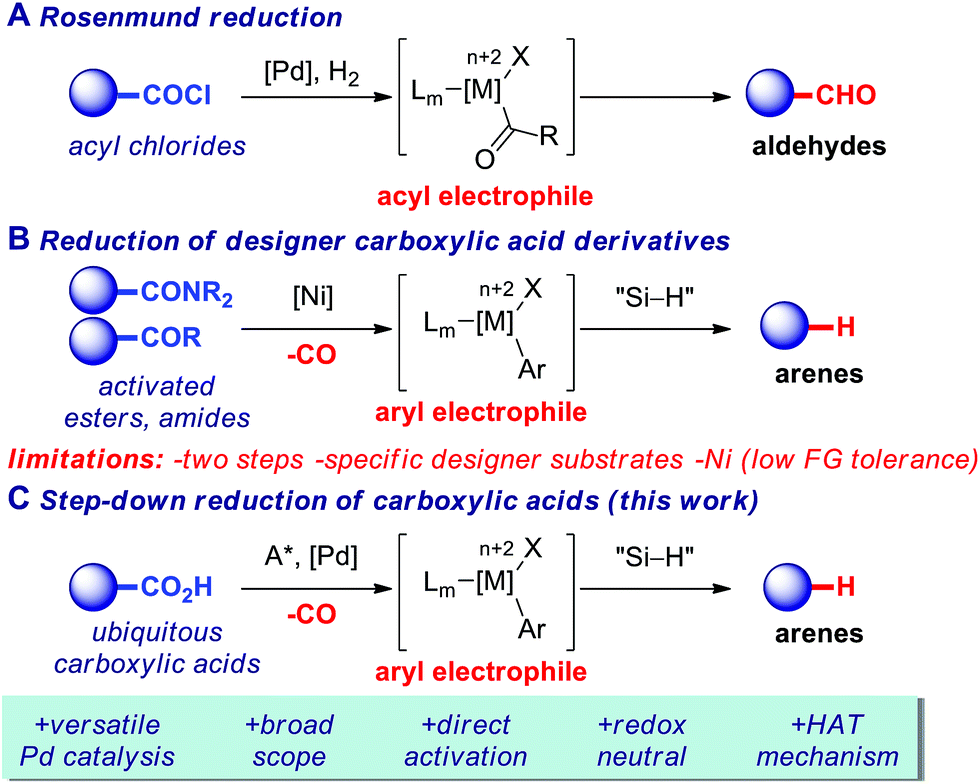
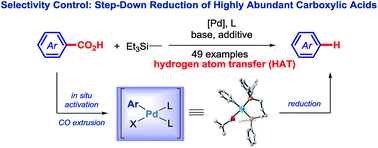
A Practical Catalytic Reductive Amination Of Carboxylic Acids Chemical Science Rsc Publishing
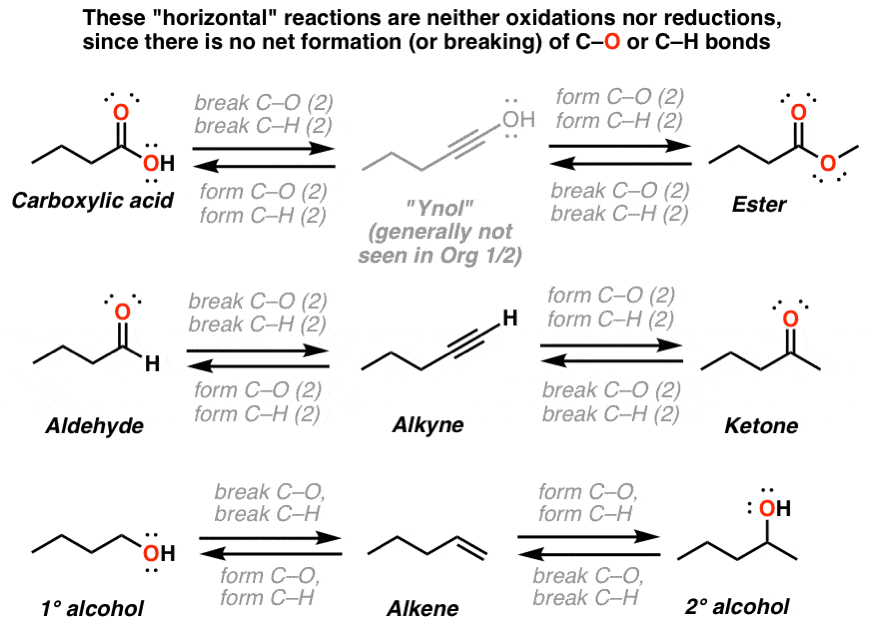


Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes are more reactive than Ketones towards nucleophilic additions The molecular mass of the compound is 86 It does not reduce Tollens' reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid ( Aldehydes Ketones andTherefore, aldehydes reduce more easily than ketones and require milder reagents and milder conditions Carboxylic acids and esters are further stabilized by the presence of a second oxygen atom which can donate a lone pair into the already polar C=O bondCarboxylic acids > sulfonic acids > acid derivatives > sulfonic acid derivatives > Nitriles > Aldehydes > Ketones Finally groups having single bond with heteroatom include alcohols (O) and amines (N) Alcohols have more elctronegative atom (O) than amines (N) and more preferred So, final order is carboxylic acids > sulfonic acids > acid



Lithium Alumnium Hydride Lialh4 Reduction Mechanism Examples



Lialh4 And Nabh4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
Example 1 Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry Methane represents the completely reduced form of an organic molecule that contains one carbon atom Sequentially replacing each of the carbonhydrogen bonds with a carbonoxygen bond would lead to an alcohol, then an aldehyde, then a carboxylic acid (discussed later), and, finally, carbon dioxideRead PDF Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Iecqa from an aldehyde, you can quite easily produce relatively complicated molecules like 2amino acids the amino acids which are used to construct proteins addition to aldehydes and ketones chemguide Carboxylic acids C n H 2n1 COOH COOH Those with only carboncarbon single bonds are3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to Describe the structure and properties of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters;



Mcat Unit 3 Chem Phys Flashcards Quizlet



Lialh4 And Nabh4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
Reductions of carboxylic acid derivatives might be expected to lead either to aldehydes or alcohols, functional groups having a lower oxidation state of the carboxyl carbon Indeed, it was noted earlier that carboxylic acids themselves are reduced to alcohols by lithium aluminum hydride At this point it will be useful to consider three kinds of reductions(ii) The release of a proton from carboxylic acid is much easier than phenols because carboxylate ion is much more resonance stabilized than phenoxide ion (b) (i) WolffKishner reduction reaction The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding hydrocarbons by heating them with hydrazine and KOH or potassium tertbutoxide in aOQ Chemicals will implement a global sales control program for Carboxylic Acids and Aldehydes until further notice OQ Chemicals employs more than 1,400 people worldwide and is part of OQ, an
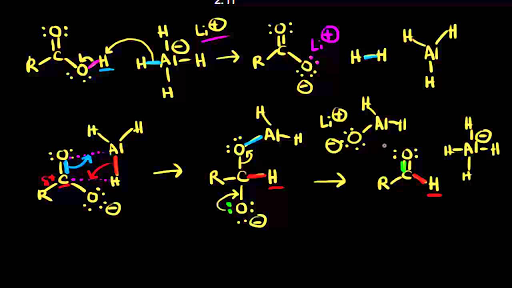


Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids Video Khan Academy
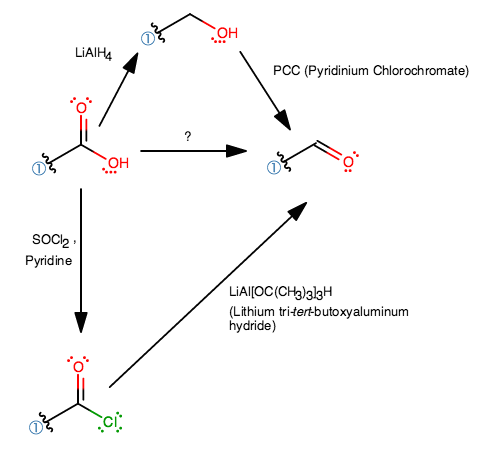


How Do You Make Aldehyde From Carboxylic Acid Socratic
Reduction of Carboxylic Acids The carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid is even more electrophilic than the carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde or ketone However, there is also an acid proton from the carboxylic acid that can react with hydride reagents For this reason, sodium borohydride does not reduce a carboxylic acidSince delocalization of benzene electrons contributes little towards the stability of phenoxide ion therefore, carboxylate ion is much more resonance stabilized than phenoxide ion Thus, the release of a proton from carboxylic acids is much easier than from phenols In other words, carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenols


Borohydride Reduction



Carboxyl Group Carboxylic Acid Reactions Uses Examples



Methods Of Preparation Of Carboxylic Acid From Alcohols Aldehydes Etc



Does Dibal H Reduce Carboxylic Acids Chemistry Stack Exchange


3 Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry


Alcohol Synthesis By Reduction Of Aldehydes And Ketones Chemistry Portal



Reading Guide 21 1 21 5 Chem 351 Studocu



Ch105 Chapter 9 Organic Compounds Of Oxygen Chemistry



Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry For Majors



Carbonyl Reduction Wikiwand


Chapter 10 Notes
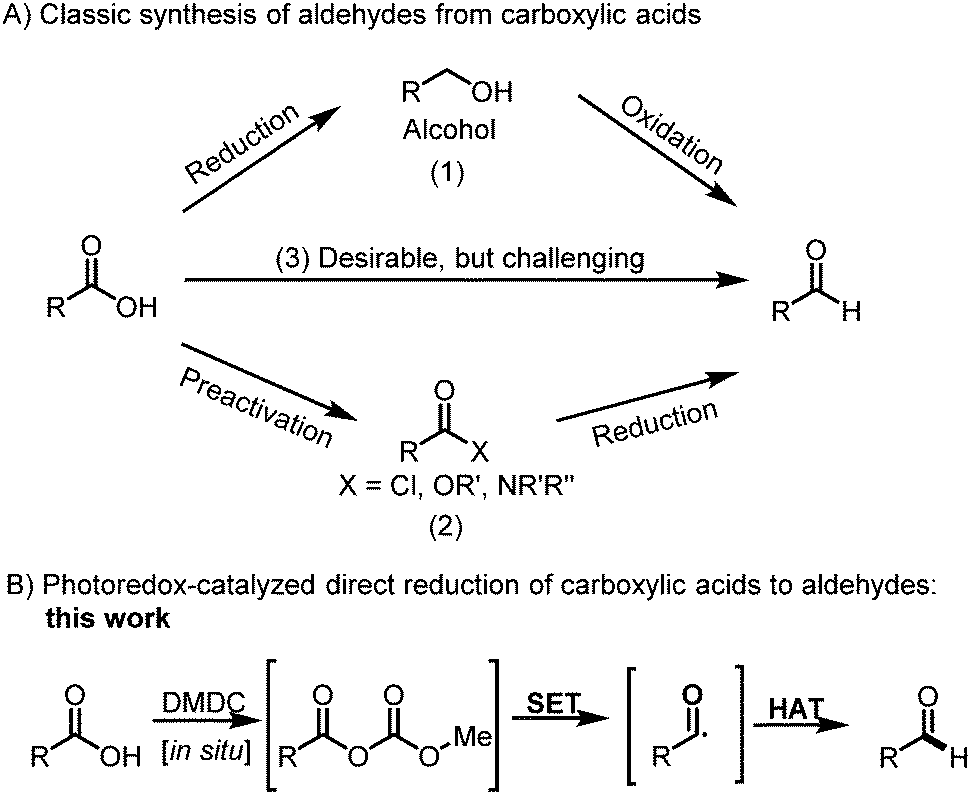


Selective Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aldehydes With Hydrosilane Via Photoredox Catalysis Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing



Carboxylic Acids An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Aldehyde And Ketones Lec 10 Introduction Aldehydes And Ketones Are Characterized By The Presence Of The Carbonyl Group Perhaps The Most Important Functional Ppt Download


Chapter 4 Carboxylic Acids Esters Che 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library



Chapter 3 Ketones And Aldehydes Flashcards Quizlet



Aldehydes Ketones Notes



Answered Aldehydes Are More Reduced Than Bartleby



Carbonyl Reduction Wikiwand


Carbonyl Reactivity


Solved Question 15 Carboxylic Acids Boil At Considerably Chegg Com


Alcohol Oxidation Strong Weak Oxidants Master Organic Chemistry
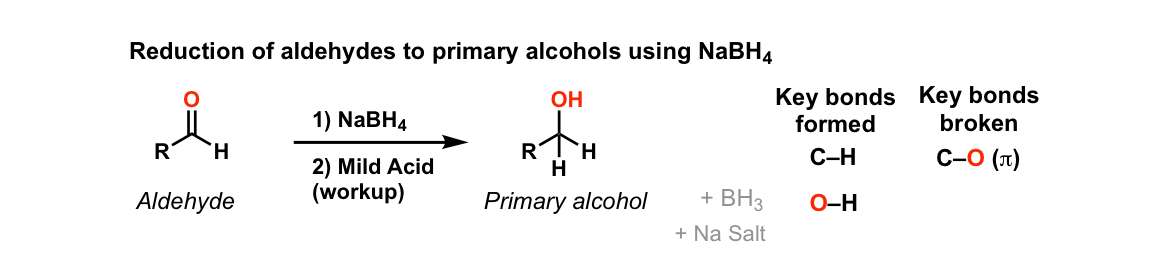


Addition Of Nabh4 To Aldehydes To Give Primary Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry



Carbonyl Reduction Wikipedia
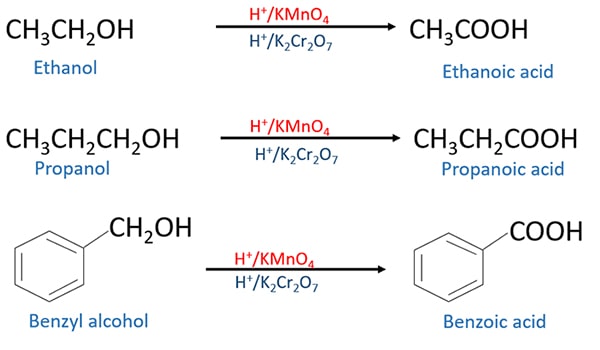


Oxidation Of Alcohols To Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic Acid
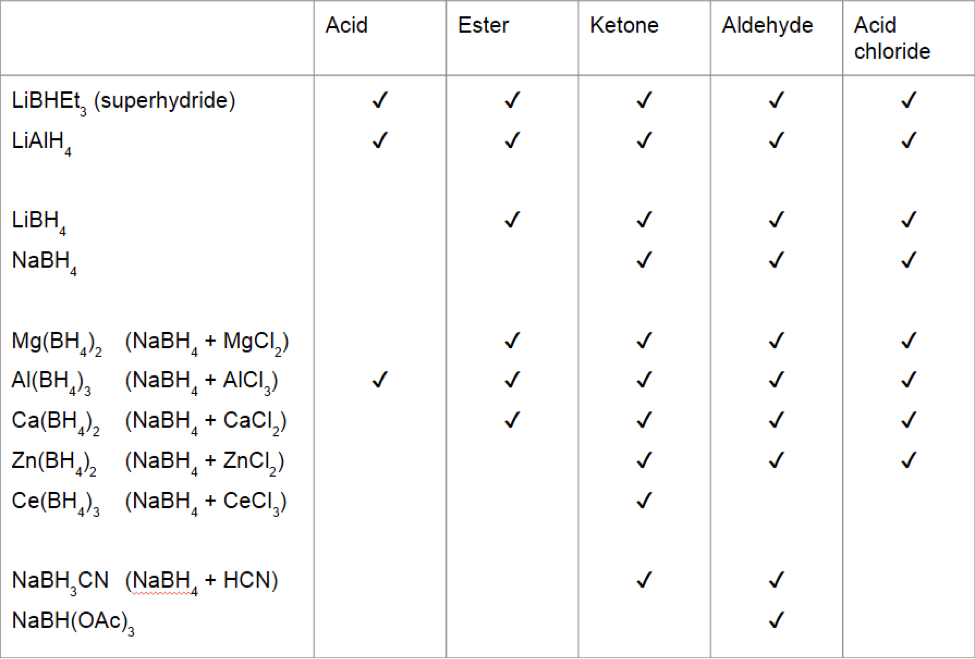


Carbonyl Reduction Wikipedia



Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry For Majors
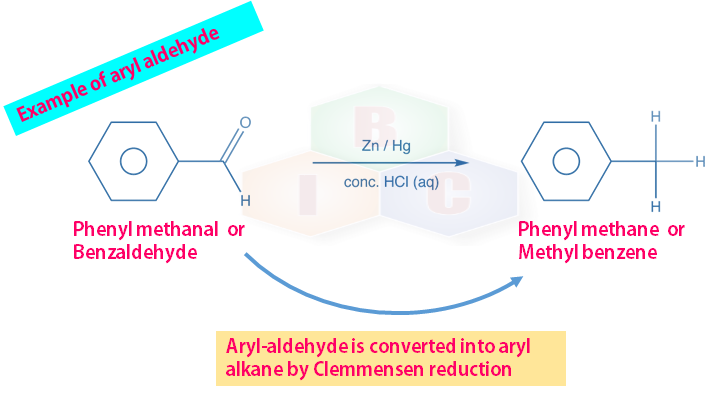


Clemmensen S Reduction Clemmensen Reduction Is An Organic By Bicpuc Medium
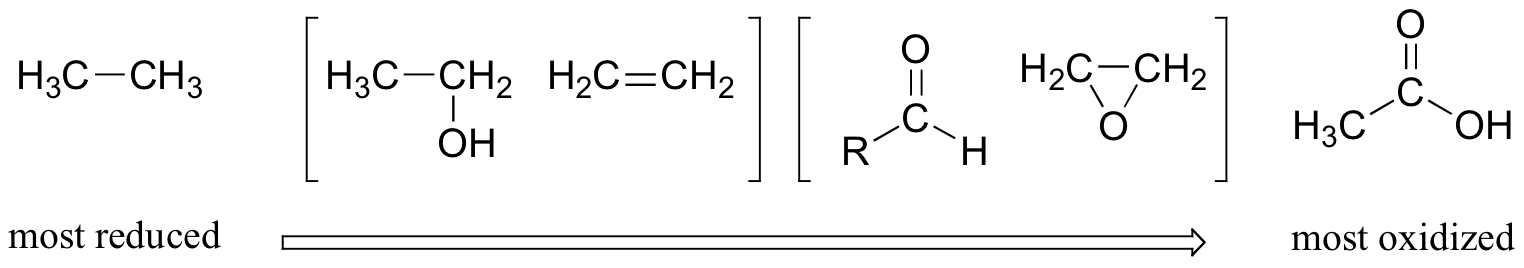


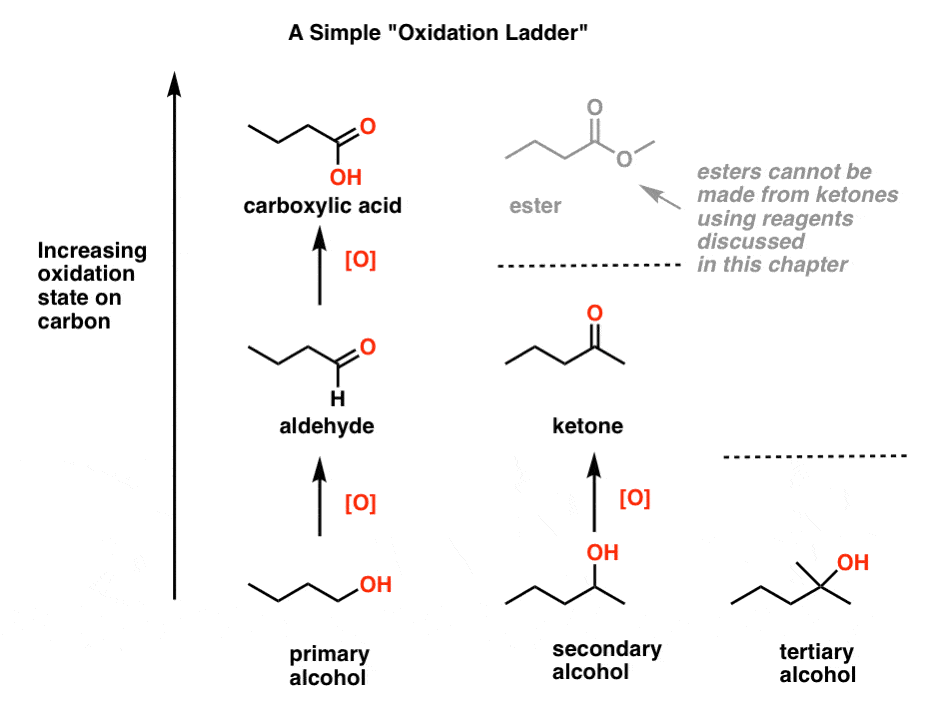
14 5 Oxidation States Of Alcohols And Related Functional Groups Chemistry Libretexts



Nabh4 Lialh4 Dibal Reduction Mechanism Carboxylic Acid Acid Chloride Ester Ketones Youtube



Lialh4 Ester Reduction Mechanism Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Chemistry Lessons



Carboxylic Acid Structure Properties Formula Uses Facts Britannica


A Level Redox 3 Oxidation Reduction Organic Chemistry Preparations Oxidation States Of Carbon In Organic Compounds Formation Reactions Gce Ks5 Revision Notes
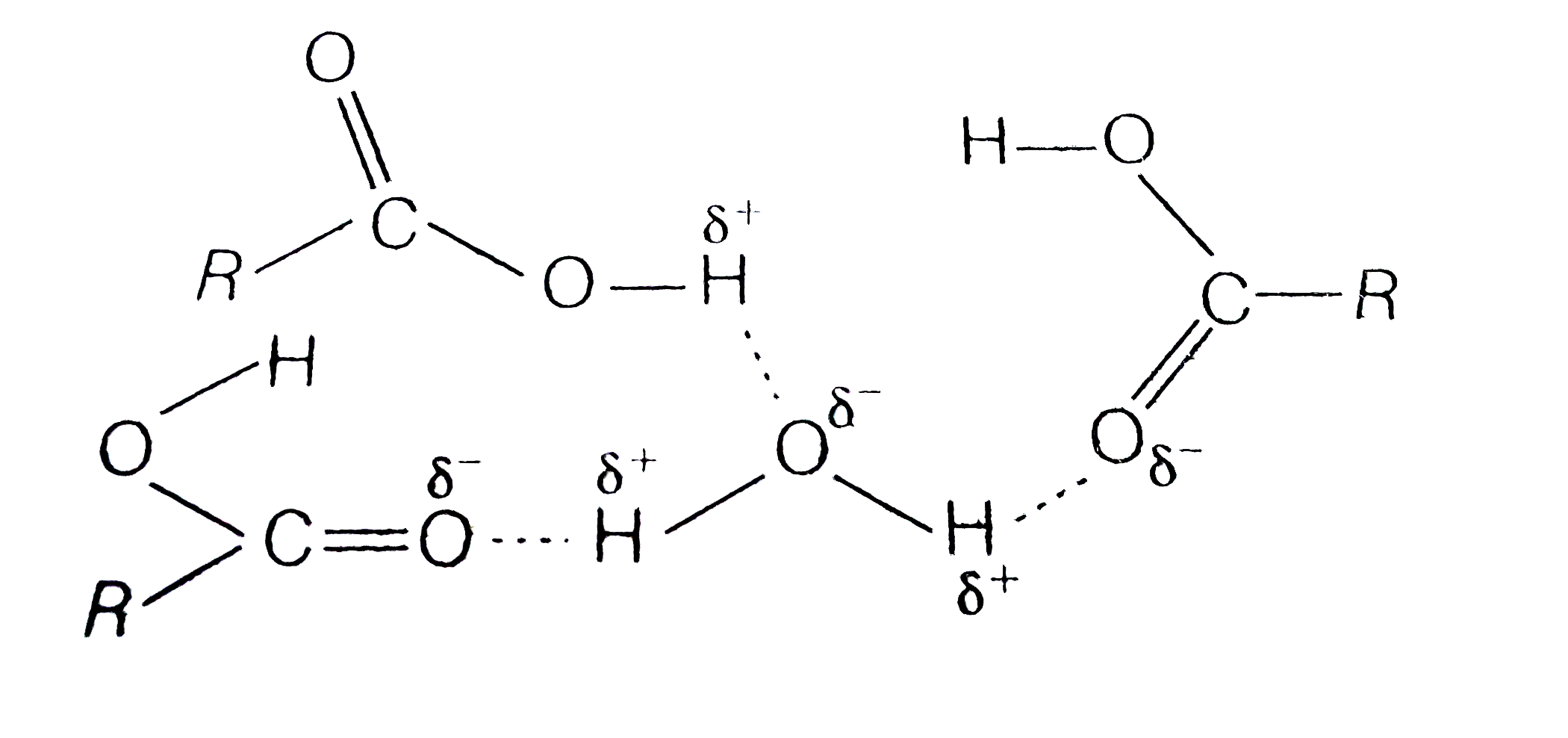


Carboxylic Acid Have Higher Boiling Points Than Aldehydes Ketone
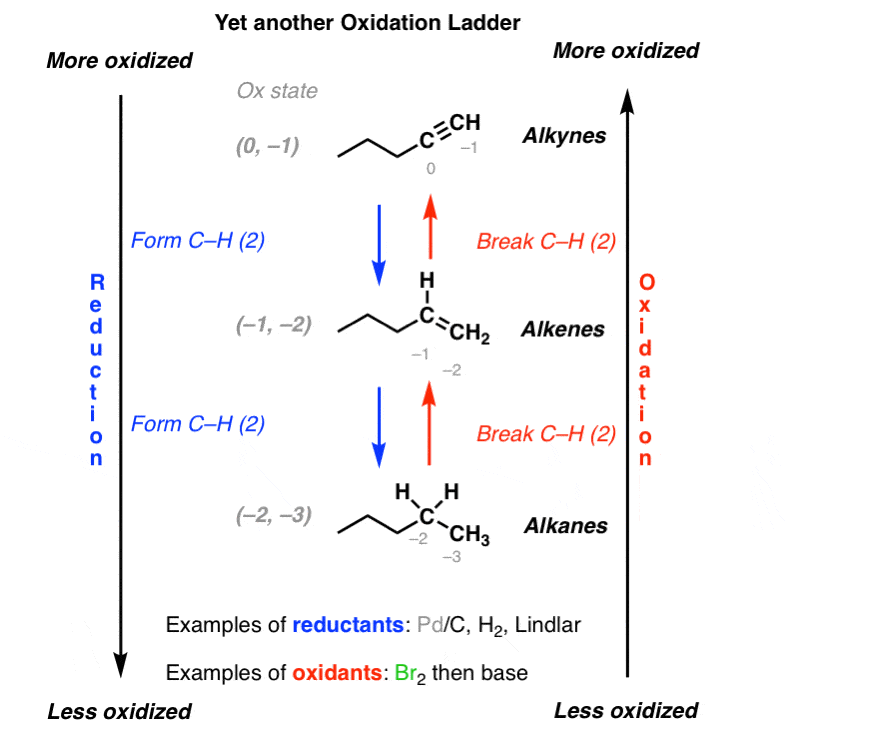


Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry



Why Are Carboxylic Acids More Acidic Than Alcohols Or Phenols Alth



Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions



Why Does Lialh4 Reduce Esters Amides Or Carboxylic Acids While Nabh4 Cannot Reduce Them Quora
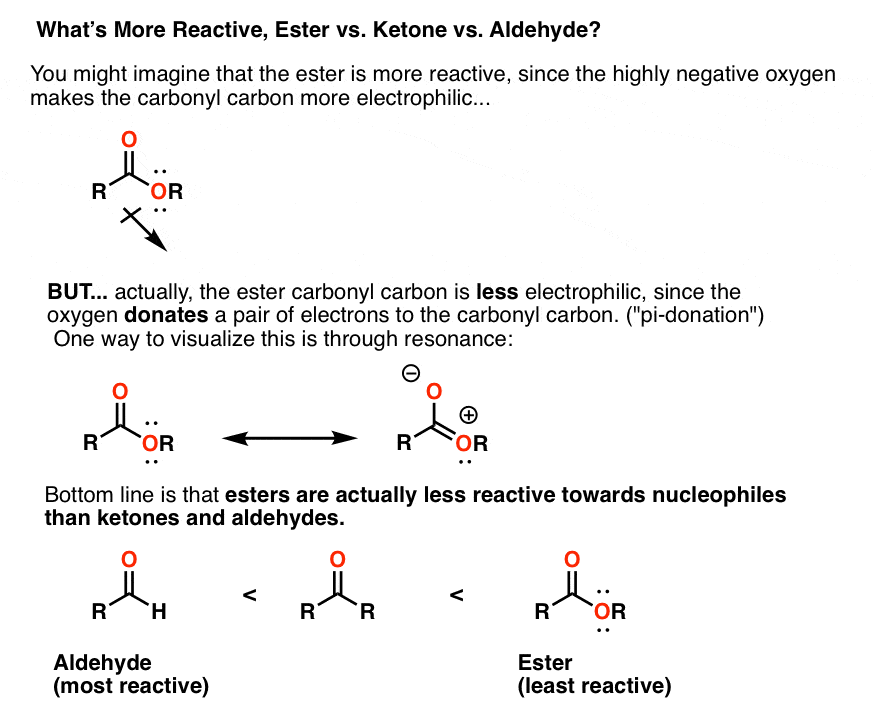


Reactions Of Grignard Reagents Master Organic Chemistry



Carboxylic Acid Reduction Britannica


Ch Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
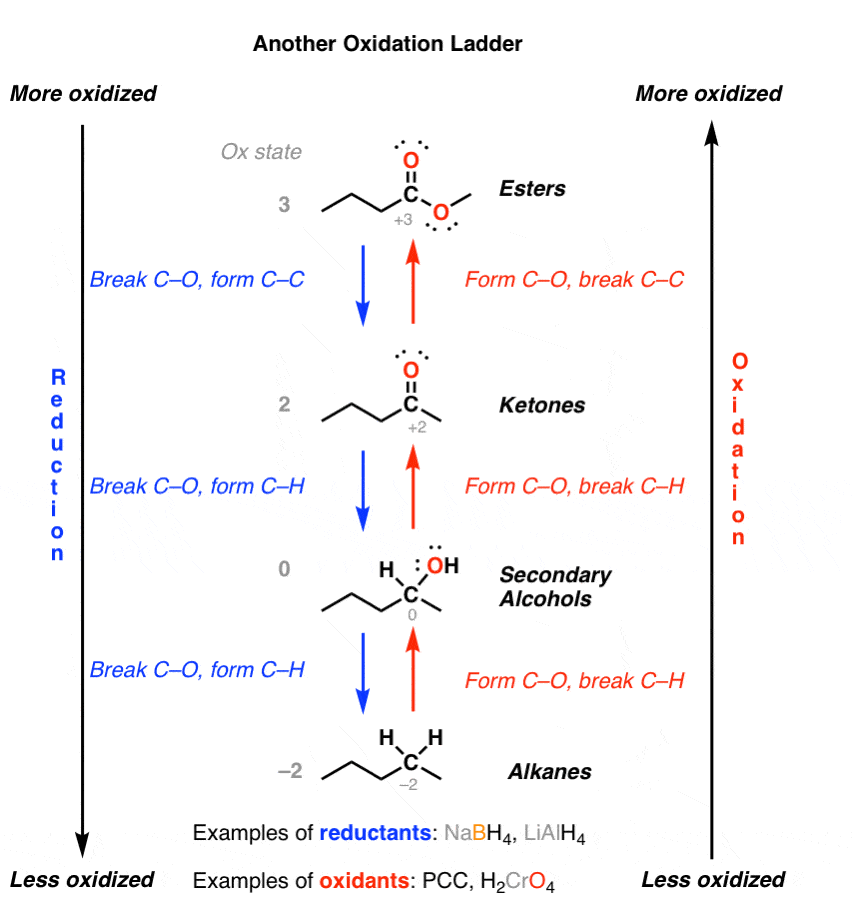


Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry



Engineering Carboxylic Acid Reductase For Selective Synthesis Of Medium Chain Fatty Alcohols In Yeast Pnas



Lialh4 And Nabh4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
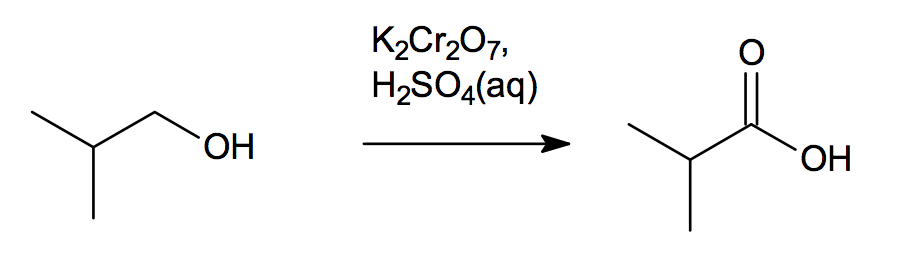


Preparation Methods Of Carboxylic Acids Definition Examples Diagrams



Ncert Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Learn Cbse
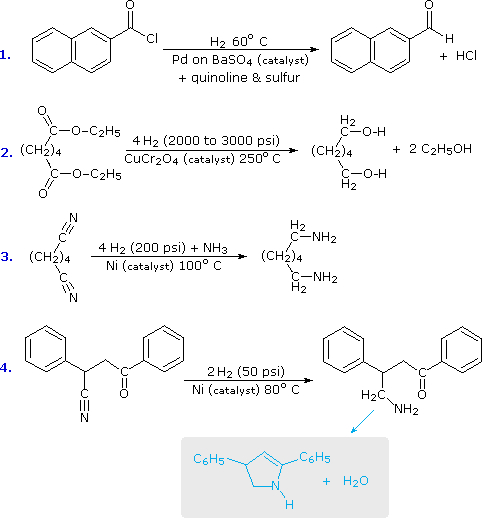


Carboxylic Derivatives Reduction Catalytic Reduction Chemistry Libretexts



Oxidation Of Alcohols Aldehydes And Ketones Ppt Video Online Download



Carboxylic Acid Have Higher Boiling Points Than Aldehydes Ketones And Even Alcohol Of Youtube


Why Are The Aldehydes More Easily Oxidized Than The Ketones Quora



Selective Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aldehydes With Hydrosilane Via Photoredox Catalysis Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing
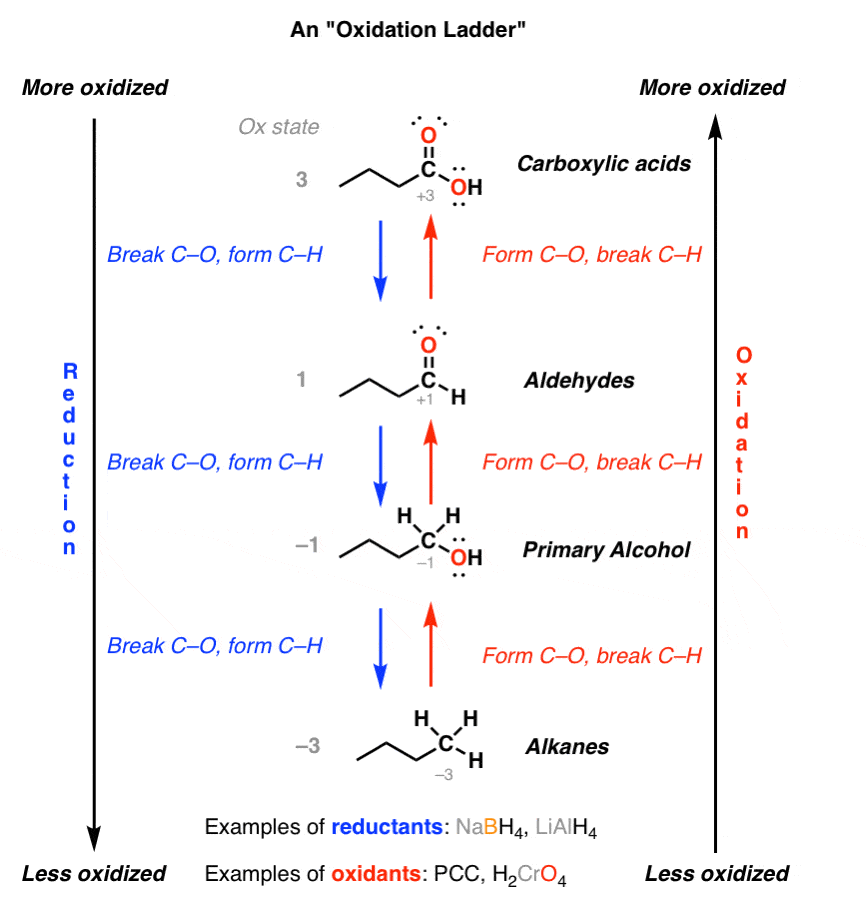


Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry
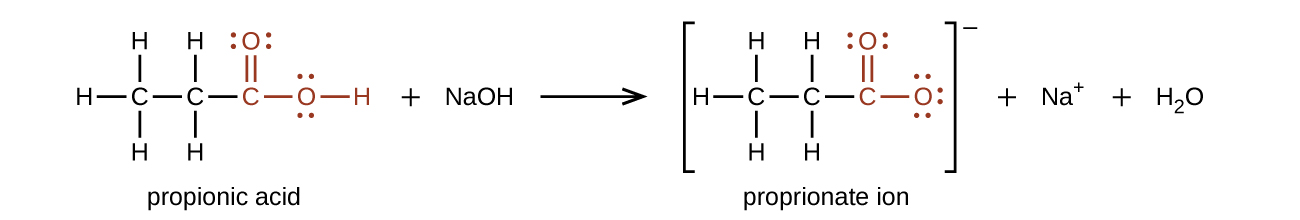


3 Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry Libretexts



Aldehyde Oxidation Reduction Reactions Britannica



Oxidation Of Alcohols To Aldehyde Ketone And Carboxylic Acid Youtube



Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry For Majors



Aldehydes Ketones Reaction Mechanisms Study Com


Lecture 21



Aldehydes Ketones Notes



Aldehydes Ketones Introduction Nomenclature Methods Of Preparation Of Aldehydes And Ketones Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones Important For Ugc Net Upsc Cse Ssc Flexiprep


Solved Ch 2 Which Of The Following Has The Lowest Pk Va Chegg Com



Properties Of Aldehydes And Ketones



Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids


Borohydride Reduction



Jones Oxidation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Ch15 Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids And Esters Using Lialh4 To 1o Alcohols


